Department of Cell Biology
 Head: Prof. RNDr. Ivan Raska, DrSc.
Head: Prof. RNDr. Ivan Raska, DrSc.
Scientists:
RNDr. Helena Fidlerova, CSc.
RNDr. Karel Koberna, CSc.
RNDr. Jan Malinsky, Ph.D.
Dr. Evgeny Smirnov, Ph.D.
Ph.D. Students:
Mgr. Zuzana Cvackova
Mgr. Marketa Fialova
Mgr. Anna Ligasova
Ing. Martin Masata
Mgr. Jaromira Vecerova
Technical Assistants:
Zdenka Fischlova
Jan Fischer
Katerina Marsickova
Vaclava Rohlenova
Simona Rysava
Lucie Tomsikova
Address:
Albertov 4, 128 01 Prague 2, Czech Republic
Phone: (+420) 224 910 315 or 224 916 248
Fax: (+420) 224 917 418
E-mail: lge@lf1.cuni.cz
The structure and functional organization of the cell nucleus remain the subjects of extensive debate today.
Understanding in molecular detail the organizing principles of the nucleus, such as the arrangement of chromosomal DNA, or the coordination and regulation of the
synthesis, processing, assembly and transport of macromolecules, are major goals for cell biology. For many years, studies on the cell biology of the
nucleus were limited by a relative lack of distinctive substructures revealed by microscopy and amenable to biochemical purification. When a typical mammalian
nucleus is observed in the electron microscope, clumps of heterochromatin are visible at the nuclear periphery and the nucleolus is readily identified by virtue
of its electrondense appearance, but otherwise the nucleoplasm appears rather featureless and amorphous. However, a very different view is evident when antibody
or hybridization probes are used to detect specific nuclear factors or genes. Many nuclear macromolecules are localized to distinct regions and substructures
of the nucleus. A specific inquiry into the role of several of these domains and nuclear substructures in RNA metabolism and other nuclear functions is the principal
aim of endeavour of the Department of Cell Biology. A useful tool for the investigation of nuclear architecture are human autoantibodies,
which are a major source of antinuclear specific probes. Importantly, the Department has a tight collaboration with the Laboratory of Gene Expression of the 1st Faculty
of Medicine of Charles University. It is worthy of mention that the Department organized two EMBO nuclear workshops in 1999 and 2002, two EMBO practical electron
microscopy courses in 1996 and 1997, and it will coorganize another EMBO course in Ceske Budejovice in 2003.
Current research addresses the following:
- Functional architecture of the nucleolus
- Nuclear architecture associated with extranucleolar RNA synthesis and processing
- Chromatin, transcription, replication and repair
- Impact of autoantibodies
Functional architecture of the nucleolus
To clarify the arrangement of rRNA genes within nucleoli, we have generated a cytochemical affinity picture
of the nucleolus. Three kinds of affinity probes have been used:
1) probes to nucleolar chromatin, including rDNA sequences,
2) probes to a number of macromolecules that are directly or indirectly involved in the synthesis and processing of rRNA and the formation of preribosomes
(including GFP hybrid proteins);
3) antibodies to nucleotide analogues such as bromouridine or biotinylated cytidine, which are used to detect labeled RNA.
The results suggest the localization of transcription sites to dense fibrillar components and to the border region between these components and fibrillar centers.
Using a permeabilized cell system, we have concluded that the processing factors are assembled on pre-rRNA at the sites of transcription. Our results obtained on living
cells show that the early rRNA processing steps take place in the domains of dense fibrillar components that are spatially separated from rDNA transcription sites.
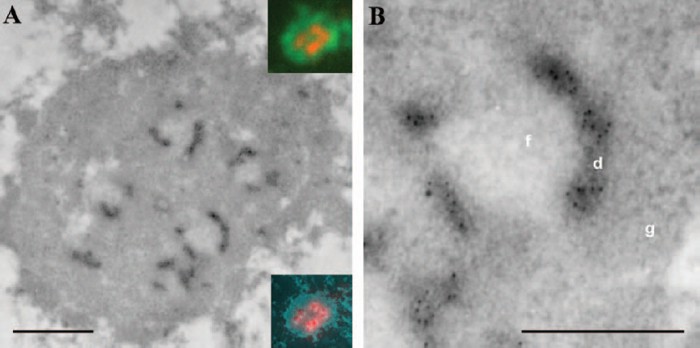
Fig.1: Concomitant light and electron microscopy mapping of transcription signal in a thin sectioned HeLa cell (B).
Detailed part of (A) .
Nuclear architecture associated with extranucleolar RNA synthesis and processing
Our results show that transcription takes place in the perichromatin regions of the nucleus and that pre-mRNA processing
is not necessarily co-transcriptional. We have provided evidence about the trafficking of released pre-mRNA transcripts to splicing factor reservoirs (nuclear speckles).
In another series of experiments, we have shown that the (pre-)spliceosomal complexes on microinjected pre-mRNA are formed inside the nuclear speckles. Their targeting
into and accumulation in the speckles are results of the cumulative loading of splicing factors to the pre-mRNA.
Chromatin, transcription, replication and repair
Replication within a replisome is a complex process, and contradictory results have been reported concerning
the mutual localization of replication and transcription sites. In order to settle this problem, a straightforward strategy was followed: a pulse with both DNA and RNA
base analogues has been detected immunocytochemically. We have developed a new procedure allowing efficient entry of BrUTP and biotinylated dUTP into living
cells. Using this approach we have shown that the signals due to the two incorporated analogues are spatially separated one from another. We have been able to
expand these findings with regard to specific genes and to show that the replicating ribosomal genes ceased to be transcribed. The obtained results have led us to
propose a switching mechanism for coordination of replication/transcription of nucleolar ribosomal genes. In this model, rRNA genes are organized in foci within nucleoli.
The foci active in replication are "switched off" for transcription, but can be "switched on" for transcription following replication. Importantly, our data point to
dynamical changes in the nucleolar architecture accompanying the switching to replication activity, as documented by the displacement of fibrillarin, a nucleolar protein
involved in the processing of rRNA, from the gene environment.
We have measured the speed of replication fork movement on extended DNA fibers labelled with the 2´-deoxythymidine analogues
5´-chloro-2´deoxyuridine and 5-iodo-2´-deoxyuridine. We show that the introduction of exogenous dNTPs accelerates the replication process at the beginning of DNA synthesis
only. The availability of 2´-deoxynucleotides seems to be a rate-limiting factor for DNA replication during early S-phase.
We have shown that DNA double-stranded breaks (dsb) produced by restriction enzymes induce the formation of foci containing replication protein
A and protein Ku on in vitro reconstituted Xenopus sperm nuclei. Such foci are involved in dsb repair and the repair of this type of DNA damage can be specifically studied
under conditions of the normal nuclear environment.
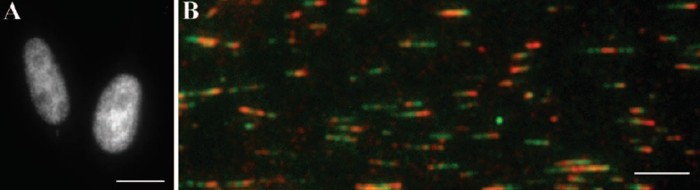
Fig. 2: Replication fluorescence pattern seen in a synchronized HeLa cell (A).
The corresponding image of the spread DNA fibres allows for the determination of the fork speed (B).
Impact of autoantibodies
The investigation of autoantibodies is important in clinical medicine. At the same time, autoantibodies
represent a major source of antinuclear probes. Our research aim is oriented to the biological characterization of autoantigens, but the results obtained are
also used for diagnostic purposes and may help in the elucidation of the etiopathogenesis of some diseases such as systemic rheumatic diseases. We
have identified an autoantibody found in the serum of a patient with systemic sclerosis and psoriatic arthritis that reacts with the core proteins of hnRNP
particle C1 and C2. Interestingly, these proteins belong to several other autoantigens cleaved by caspases during apoptosis.
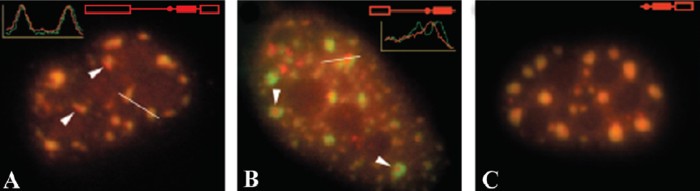
Fig. 3.: Localization of spliceable (A) and mutant (B,C) fluorochrome-labeled RNAs microinjected
into HeLa cells.
Relevant publications before 1998
1. Raska, I., Ochs, R.L., Salamin-Michel, L. (1990)
Immunocytochemistry of the cell nucleus. Electr. Microsc.
Rev. 3: 301-353
2. Raska, I., Ochs, R.L., Andrade, L.E.C., Chan, E.K.L., Burlingame, R., Peebles, C., Tan, E.M. (1990)
Association between the nucleolus and coiled body. J. Struct. Biol. 104: 120-127
3. Raska, I., Andrade, L.E.C., Ochs, R.L., Chan, E.K.L., Chang, C.M., Roos, G., Tan, E.M. (1991)
Immunological and ultrastructural studies of the nuclear coiled body with autoimmune antibodies. Exp.
Cell. Res. 195: 27-37
4. Andrade, L.E.C., Chan, E.K.L., Raska, I., Ross, G., Peebles, C.L., Tan, E.M. (1991)
Human autoantibody to
a novel protein of the nuclear coiled body. Immunological characterization and cDNA cloning of p80-coilin.
J. Exp. Med. 173: 1407-1419
5. Raska, I., Michel, L., Jarnik, M., Dundr, M., Fakan, S., Gasser, S. M., Gassmann, M., Hubscher, U.,
Isaurralde, E., Martinez, E., Richter, A., Dubochet, J. (1991)
Ultrastructural cryoimmunocytochemistry rep-
resents a convenient tool to study DNA replication in cultured cells. J. Electron. Micr. Tech. 18: 91-105
6. Raska, I., Dundr, M., Koberna, K. (1992)
Structure-function subcompartments of the mammalian cell nucle-
us as revealed by the electron microscopic affinity cytochemistry. Cell. Biol. Int. Rep., 16: 771-789
7. Dundr, M., Raska I. (1993)
Non-isotopic ultrastructural mapping of transcription sites within the nucleolus.
Exp. Cell. Res. 208: 275-281
8. Strand, D., Raska, I., Mechler, B.M. (1994)
The Drosophila l(2)giant larvae tumour suppressor protein is a
component of the cytoskeleton. J. Cell. Biol. 127: 1345-1360
9. Raska, I., Dundr, M., Koberna, K., Melcak, I., Risueno, M.-C., Török, I. (1995)
Does the synthesis of riboso-
mal RNA take place within nucleolar fibrillar centers or dense fibrillar components? A critical appraisal. J.
Struct. Biol. 114: 1-22
10. Raska, I. (1995)
Nuclear ultrastructures associated with the RNA synthesis and processing. J. Cell.
Biochem. 59: 11-26
11. Melcak, I., Risueno, M.C., Raska, I. (1996)
Ultrastructural non-isotopic mapping of nucleolar transcription
sites in onion protoplasts. J. Struct. Biol. 116: 253-263
12. Schul, W., Groenhout, B., Koberna, K., Takagaki, Y., Jenny, A., Manders, E.M., Raska, I., van Driel, R., de
Jong, L. (1996)
The RNA 3´cleavage factors CstF-64kD and CPSF-100kD are concentrated in nuclear
domains closely associated with coiled bodies and newly synthetized RNA. EMBO J. 15: 2883-2892
13. Melcak, I., Raska, I. (1996)
Structural organization of the pre-mRNA splicing commitment: a hypothesis. J.
Struct. Biol. 117: 189-194
14. Velicky, J., Titlbach, M., Duskova, J., Vobecky, M., Strbak, V., Raska, I. (1997)
Potassium bromide and the
thyroid gland of the rat: morphology, immunohistochemistry, RIA and INAA analysis. Anat. Anz. 179: 421-
431
15. Stanek, D., Vencovsky, J., Kafkova, J., Raska, I. (1997)
Heterogenous nuclear RNP C1 and C2 core pro-
teins are targets for an autoantibody found in the serum of a patient with systemic sclerosis and psoriatic
arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 40: 2172-2177
Publications 1998-2002
1. Raska, I., Pliss, A., Mandys, V., Risueño, M.C., Lojda, Z. (1998)
Processing of free cells for electron
microscopy using a fibrin clot. Acta Histochem. 100: 309-313
2. Velicky, J., Titlbach, M., Lojda, Z., Duskova, J., Vobecky, M., Strbak, V., Raska, I. (1998)
Long-term action
of potassium bromide on the rat thyroid gland. Acta Histochem. 100: 11-23
3. Koberna, K., Landa, V., Kanka, J., Pliss, A., Eltsov, M., Stanek, D., Raska, I. (1998)
Non-isotopic detection
of nucleolar transcription in pre-implantation mouse embryos. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 38: 117-126
4. Gonzalez-Melendi, P., Testillano, P.S., Mena, C.G., Müller, S., Raska, I., Risueño, M.C. (1998)
Histones
and DNA ultrastructural distribution in plant cell nucleus: a combination of immunogold and cytochemical
methods. Exp. Cell Res. 242: 45-59
5. Raska, I., Reimer, G. (1999)
Human autoantibodies identify a protein in dense fibrillar and granular components
of the nucleolus. Acta Histochem. 101: 157-166
6. Pliss, A., Raska, I., Eltsov, M. (1999)
Presence of actin in nuclei of rat NBT II cells. In: Fluorescence
microscopy and fluorescent probes (A. Kotyk, ed), Espero Press, 1999, ss. 223-234
7. Koberna, K., Stanek, D., Malinsky, J., Eltsov, M., Pliss, A., Ctrnacta, V., Cermanova, S., Raska, I. (1999)
Nuclear organization studied with the help of a hypotonic shift: its use permits hydrophilic molecules to
enter into living cells. Chromosoma 108: 325-335
8. Stanek, D., Kiss, T., Raska, I. (2000)
Pre-ribosomal RNA is processed in permeabilised cells at the site of
transcription. Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 79: 202-207
9. Koberna, K., Stanek, D., Malinsky, J., Ctrnacta, V., Cermanova, S., Novotna, J., Kopsky, V., Raska, I.
(2000)
In situ fluorescence visualization of bromouridine incorporated into newly transcribed nucleolar
RNA. Acta Histochem. 102: 15-20
10. Melcak, I., Cermanova, S., Jirsova, K., Koberna, K., Malinsky, J., Raska, I. (2000)
Nuclear pre-mRNA compartmentalization:
trafficking of released transcripts to splicing factor reservoirs. Mol. Biol. Cell. 11: 497-510
11. Testillano, P.S., Coronado, M.J., Segui, J.M., Domenech, J., Gonzalez-Melendi, P., Raska, I., Risueño,
M.C. (2000)
Defined nuclear changes accompany the reprogramming of the microspore to embryogenesis. J. Struct. Biol. 129: 223-232
12. Benoist, P., Feau, P., Pliss, A., Vorisek, J., Antonelli, R., Raska, I., Denis-Duphil, M. (2000)
The yeast Ura2
protein that catalyses the first two steps of pyrimidines biosynthesis accumulates not in the nucleus but in
the cytoplasm, as shown by immunocytochemistry and Ura2-green fluorescent protein mapping. Yeast, 16:
1299-1312
13. Raska, I., Aebi, U., Earnshaw,W.C. (2000)
EMBO workshop report. An eclipse over the cell nucleus.
Functional organization of the cell nucleus. Prague, August, 9-12, 1999. EMBO J. 19: 3843-3848
14. Eltsov, M., Grandi, P., Raska, I. (2000)
Ultrastructural characterization of RPA-containing domains in nuclei
assembled in Xenopus egg extracts. J. Struct. Biol. 129: 211-217
15. Raska, I. (2000)
The Cell Nucleus. Vesmir, 79: 562-572
16. Müller, J., Tvrdik, D., Dvorak, R., Djaborkhel, R., Mandys, V., Bednar, B., Raska, I., Lojda, Z. (2000)
Expression of beta-catenins and cadherins by follicular dendritic cells in human lymph nodes. Acta
Histochem. 102: 369-380
17. Malinsky, J., Koberna, K., Stanek, D., Masata, M., Votruba, I., Raska, I. (2001)
The supply of exogenous
deoxyribonucleotides accelerates the speed of the replication fork in early S-phase. J. Cell. Sci. 114: 747-750
18. Melcak, I., Melcakova, S., Kopsky, V., Vecerova, J., Raska, I. (2001)
Prespliceosomal assembly on microin-
jected precursor mRNA takes place in nuclear speckles. Mol. Biol. Cell. 12: 393-406
19. Grandi, P., Eltsov, M., Nielsen, I., Raska, I. (2001)
DNA double-strand breaks induce formation of RP-A/Ku
foci on in vitro reconstituted Xenopus sperm nuclei. J. Cell. Sci. 114: 3345-3357
20. Stanek, D., Koberna, K., Pliss, A., Malinsky, J., Masata, M., Vecerova, J., Risueno, M.C., Raska, I. (2001)
Non-isotopic mapping of ribosomal RNA synthesis and processing in the nucleolus. Chromosoma 110:
460-470
21. Raska, I. (2001)
Opportunities in molecular medicine, with an emphasis on the situation of young scien-
tists. In: Perspectives of Science in Central and Eastern Europe (Q. Schiermeier and J. Ockenden, eds.),
NATO Science Series, IOS Press, Amsterodam, pp.69-74
22. Kopsky, V., Vecerova, J., Melcak, I., Pliss, A., Stulik, J., Koberna, K., Tomsikova, L., Raska, I. (2002)
An
ATP-Dependent Step Is Required for the Translocation of Microinjected Precursor mRNA into Nuclear
Speckles. Folia Biol., 48: 69-72
23. Politi, V., Perini, G., Trazzi, S., Pliss, A., Raska, I., Earnshaw, W. C., Della Valle, G. (2002)
CENP-C binds
the alpha-satellite DNA in vivo at specific centromere domains. J. Cell. Sci. 115: 2317-2327
24. Stokrova, J., Korb, J., Pliss, A., Raska, I., Stulik, J., Dvorakova, M. (2002)
Overexpression of v-myb onco-
gene or c-myb proto-oncogene in insect cells: characterization of newly induced nucleolus-like structures
accumulating myb protein. Int. J. Mol. Med. 9: 547-554
25. Koberna, K., Malinsky, J., Pliss, A., Masata, M., Vecerova, J., Fialova, M., Bednar, J., Raska, I. (2002)
Ribosomal genes in focus: new transcripts label the dense fibrillar components and form clusters indica-
tive of “Christmas trees” in situ. J. Cell. Biol. 157: 743-748.
26. Ruzickova, S., Pruss ,A., Odendahl, M., Wolbart, K., Burmester, G.R., Scholze, J., Dörner, T., Hansen, A.
(2002)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia preceeded by cold agglutinin disease: intraclonal Ig light chain diver-
sity in VH4-34 expressing single leukemic B cells. Blood, 100: 3419-3422
27. Pfannenschmid, F., Wimmer, V.C., Rios, R.M., Geimer, S., Haller, K., Nìmcova, Y., Mages, W. (2002)
Chlamydomonas DIP13 and human NA14: a new class of proteins associated with microtubule structures
is involved in cell division. J.Cell Sci. 116: 1449-1462
|