Projects
|
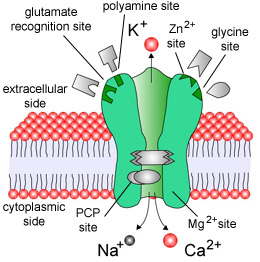
Neuroactive steroidsSynthesis of positive and negative modulators of NMDA receptor
|
|
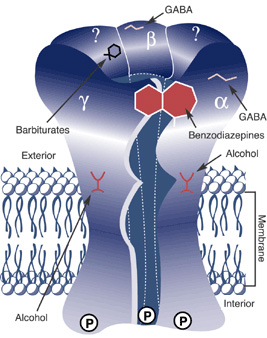
Neuroactive steroidsSynthesis of positive allosteric modulators of GABAA receptor
|
|
Steroids for other biomedical applicationsUsing cooperation with several scientific institutions, series of compounds prepared in the past as well as newly designed and synthesized derivatives are being tested for their anticancer, antiviral and antibacterial activities, active drug transport and their impact on phenotypes of selected cell lines. Compounds with interesting level of activity become form of the starting structures for the synthesis of the next generations of products. This area will partially merge into the above mentioned steroid fluorescent labelling research. We will take advantage of the acquired findings of suitable labels and methods of their synthesis and attachment. |