Projects
|
Research area of Prof. P. HobzaNon-covalent InteractionsTheoretical studies on stabilization energy, structure, geometry, properties and nature of stabilization on different types of noncovalent interactions: H-bonding; improper - blue shifting - H-bonding; dihydrogen bonding; halogen bonding; stacking; dispersion bonding. |
Development of nonempirical ab initio quantum chemical methods for calculation of noncovalent interactionsWith ever growing amount of information about the accuracy and applicability of various (low-order scaling) methods for calculation of noncovalent complexes, we can focus on the weak points of these methods and eventually propose a ways to increase their accuracy, applicability and reliability. Scaled perturbation theories, spin-component scaled methods and hybrids of density functional and wave function theories are currently investigated. Development of semiempirical QM methods describing noncovalent interactionsSemiempirical QM methods are potentially very useful tool for study of large biomolecules, as their ability to describe quantum mechanical effects makes them superior to widely used molecular mechanics. However, these methods fail to describe properly noncovalent interactions - hydrogen bonds and dispersion, and these interactions often determine the structure and function of biomolecules. We have developed corrections to several semiempirical methods that allow to achieve chemical accuracy in description of these interactions. Accurate calculation of noncovalent interaction energies and geometriesHighly accurate data on noncovalent complex properties, like the binding energy or its geometry present extremely valuable information not only for the proper understanding of the nature of the particular interaction, but also for development and testing of new, computationally more efficient approximate methods. In this respect, demanding coupled-cluster or other highly-correlated calculations have to be carried out. This is, considering the size of the biologically relevant species, a challenge for both the computer hardware and the software. Highly parallelized algorithms mainly in coupled-clusters and perturbation theories are being developed or optimized, utilization of the graphical processing units is also of a great interest for the future. Many-body effects in noncovalent interactionsProper description of many-body effects (also called "cooperativity" or "nonadditivity") in noncovalent complexes with a significant contribution form the dispersion energy is an extremely difficult task for computational chemistry, since the most sophisticated (thus the most demanding) computational methods have to be applied. A lot of the phenomena caused the many-body effects in, for instance, biology is still not revealed, mainly due to the oversimplification of models used in the past. Possible consequence of many-body effects on the geometry of the DNA or peptides are currently being studied. Thermodynamic characteristicsThe biologically relevant systems need to be described not only by means of the interaction energy but also by means of the free energy and entropy, respectively. These thermodynamic quantities are conveniently accessible through molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and advanced MD techniques. Particular attention is paid to an investigation of the DNA...ligand and protein...ligand complexes, to the role of solvent in the binding processes and solute conformational changes, all forward to the potential medicinal utilisation. Systematic exploration of complex potential energy surfacesRecent development in reaction path search algorithms allowed us to characterize reaction paths and transition states in systems of remarkable complexity. Systematic, combinatorial approach is used to determine all minimum energy paths connecting thermodynamically accessible minima. Currently, we are applying this methodology to conformation changes in biomolecular clusters and model peptides. Theoretical description of biologically relevant systems in electronically excited statesStudy of dynamics of electronically excited states of nucleic acids bases and their analogues using “on-the-fly” approach based on ab initio multireference methods. Study of the nature of noncovalently bonded biologically relevant complexes in their electronically excited states with the goal to investigate the structure and dynamics of defects generated by UV light. In silico drug designSemiempirical PM6-DH2 method, which was recently developed in our laboratory and which accurately describes H-bonding as well as dispersion energy, is used as a scoring function in virtual screening. Protein…ligand binding free energy is constructed as a sum of protein…ligand gas-phase binding free energy, change of hydration free energies, deformation energy and entropic term. When the crystal structure of a protein…ligand complex is not available some of docking algorithms are applied. |
|
|
Research area of O. BludskýProbe molecules (e.g., CO, H2) are often used for characterization of complex molecular environments (molecular sieves, molecular matrices). Assignment of spectral characteristics to particular structure is difficult and in many cases impossible. Our goal is to link the spectral features to particular structure type based on the overlap of experimental and theoretical spectra. |
|
Research area of M. Kabeláč
|
|
Research area of P. NachtigallMetal-exchanged zeolites (M+/zeolite) are intensively investigated for their interesting sorption and catalytic properties. We investigate the coordination and localization of metal cation sites in zeolites and their interaction with adsorbed molecules. The period DFT or a hybrid QM/MM models are used for the description of the system. Metal cation sites in zeolites with different topology (including MFI, FER, IFR, LTA) and composition are systematically investigated. It is our goal to understand the correlation between the cation coordination and its adsorption and catalytic properties. Vibrational dynamics of molecules adsorbed on M+/zeolites is investigated theoretically. Vibrational frequencies of small molecules adsorbed inside the zeolite channels can be calculated with spectroscopic accuracy, using a recently developed ω/r scaling method together with the periodic model of zeolite. Therefore, details of experimental IR spectra can be interpreted based on these calculations. Theoretical investigation of properties of Cu-containing zeolites, in particular, electronic excitation energies (UV-vis spectra), vibrational dynamics of adsorbed probe molecules, and catalytic activity. |
|
|
Research area of D. NachtigallováThe behavior of nucleic acid bases in their excited states has been subject of several experimental and theoretical studies. The aim of these studies is to explain their photochemical behavior in order to prevent the nucleic acid bases against UV damage. In our group we are interested in the calculations of electronically excited states of nucleic acid bases in the stacked conformation to investigate the excited state energy transfer between DNA bases. The aim of these studies is to evaluate the interaction of DNA bases in their excited states depending on the sequence of bases and their mutual orientation. The calculations of the relevant small models are also performed to understand these phenomena based on the results obtained with precise methods which are not always possible in the calculations of DNA bases. |
|
Research area of V. ŠpirkoQuantum-mechanical studying of large molecular rearangements opposed by nonharmonic (multiple minima) potential energy functions (conformational dynamics, isomerizations, proton transfers, dynamical corrections for molecular properties). Theoretical studying of highly excited and continuum ro-vibrational states of small molecular systems (density and statistical properties of molecular states, energy clustering and "hidden" symmetries, elementary chemical reactions). Approximate methods for quantum-mechanical calculations (adiabatic separation approaches, numerical integration of coupled Schrödinger equations). |
|
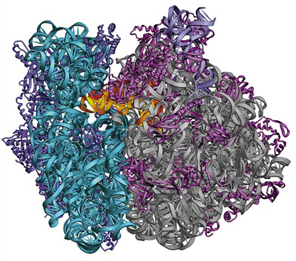
Research area of J. ŠponerComputational chemistry of nucleic acids, structural molecular biology and biophysics, molecular modeling, atomistic simulations of biopolymers, quantum chemistry, bioinormatics. Structural studies of functional RNA molecules. These studies include investigations of several ribozymes (Hepatitis Delta Virus r., Hairpin r. and Hammerhead r.) and are presently aimed towards MD and QM/MM analyzes of the reaction mechanism. Major attention is paid to structural dynamics of key ribosomal RNA segments, such as the A-site finger, L7/L12 stalk and L1 stalk, which play essential role in tRNA binding and movement throughout ribosome during protein synthesis. Studies of DNA (B-DNA, quadruplexes and others) and their complexes with drugs and proteins. Theoretical studies of the basic principles of molecular interactions of nucleic acids including metal cation interactions, with a special attention paid to RNA folding. |
|
|
Research area of J. Vondrášek
|