Equipment
PE 2400 Series II CHN AnalyzerThe PE 2400 Series II CHNS/O Analyzer (Perkin Elmer, USA) serves for simultaneous determination of C, H, and N in organic compounds. In the CHN operating mode the instrument employs a classical combustion principle to convert the sample elements to simple gases (CO2, H2O and N2). The PE 2400 analyzer performs automatically combustion and reduction, homogenization of product gases, separation and detection. A microbalance MX5 (Mettler Toledo) is used for precise weighing of samples. The accuracy of CHN determination is better than 0.30% abs. The instrument was installed in 1999.
AUTOPOL IVThe AUTOPOL IV (Rudolph Research Analytical, USA) is a microprocessor based automatic polarimeter for measurement of optical rotation (±89° Arc), specific rotation ±999.99° Arc) and concentration (0 - 99.9%). The Autopol IV comprises Glan Thomson calcite quartz prism polarizer. The highest resolution is 0.001° Arc for optical rotation, 0.001° below 90° Arc and 0.01° between 100 to 999.99° Arc for specific rotation and 0.001% for concentration. However, usually the resulting values of specific rotation are given with one decimal place. The polarimeter accepts sample cells up to 200 mm. The instrument was installed in 2001.
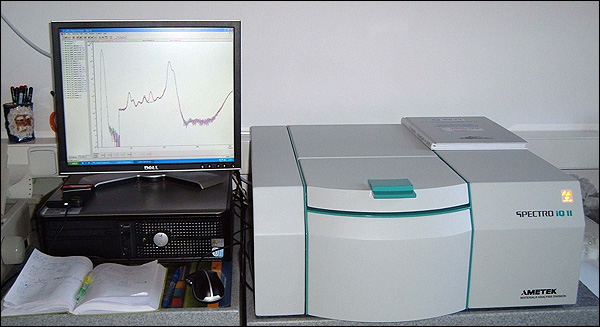
SPECTRO iQIIThe simultaneous energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence benchtop spectrometer SPECTRO iQ II (Spectro Analytical Instruments, Germany) was purchased in 2008. The samples are excited by a forced air-cooled low-power Pd end-window X-ray tube combined with a doubly curved HOPG crystal for monochromatization and polarization of the primary tube radiation. A VITUS-Silicon Drift Detector (SDD) with Ta collimator is used to collect the fluorescence emission from the sample. The resolution of the SDD is better than 160 eV for Mn Kα. All radiation paths are flushed with helium. The measurement parameters are controlled by the system PC. The SPECTRO iQ II spectrometer allows a non-destructive simultaneous multi-element both qualitative and (after development of calibration method) quantitative analysis of elements from Na to U in different types of sample forms (except gases).
|