DETAILS OF THE ACHIEVEMENT
| Plasmonic nanostructures for optical biosensing |
| Assoc. Prof. Jiří Homola, Ph.D., DSc. |
| Year: 2011 |
Label-free biosensors represent a disruptive technology that enables
the direct observation of biomolecular interactions in real-time and
rapid and sensitive detection of chemical and biological species with
potential applications in areas such as medical diagnostics,
environmental monitoring and food safety. Optical biosensors based on
surface plasmons represent the most advanced and mature label-free
photonic biosensor technology. Researchers at the Institute of
Photonic and Electronics, AS CR, v. v. i. have investigated various
types of plasmonic nanostructures to further improve performance and
expand utility of plasmonic biosensors. In collaboration with
researchers at the University of Washington, Seattle (USA), they
researched special quasi-3D nanostructures consisting of thin metal
films with nanoholes separated from a layer of metal nanodiscs that
face nanoholes by a thin dielectric layer [1, 2]. It was demonstrated
that Fabry-Pérot resonances in these structures allow for achieving
strong localization of the electromagnetic field which makes the
structures attractive for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)
[2]. Sensing properties of plasmonic nanoparticle arrays have been
investigated in collaboration with the Karl-Franzens University Graz
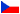
(Austria). We have investigated the local sensitivity of gold nanorods
to changes in the refractive index both theoretically and
experimentally and demonstrated that the spatial distribution of
sensitivity matches the profile of electric field intensity [3]. We
have developed a new biosensor based on an array of gold nanorods [4].
The sensor was shown to be able to detect DNA molecules at levels down
to 100 pM and the lowest detectable surface coverage corresponding to
less than one DNA molecule per nanoparticle [4].

Extinction spectra of plasmonic nanostructure consisting of an array of gold nanorods for two different refractive indices of the surrounding medium. The inset shows an SEM image of an array. |
|