6th FERO meetingASTRONOMICAL INSTITUTE
| |||||||||||
| Euro in Czech Crowns: 1€ = Kč | |||
| Metro-Tram scheme | |||
| Map of centre (more detailed) | |||

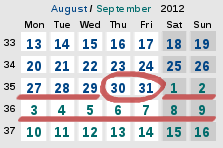
6th FERO meetingASTRONOMICAL INSTITUTE
| |||||||||||
| Euro in Czech Crowns: 1€ = Kč | |||
| Metro-Tram scheme | |||
| Map of centre (more detailed) | |||

