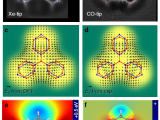
3D x-ray diffraction method at ESRF Grenoble (ID11 beamline) was applied to investigate grain resolved internal stress and strain around the martensite band front propagating in 0.1mm thin superelastic NiTi wire deformed in tension, We reconstructed internal stress and strain fields around the front and performed simulation by finite element implements SMA model. In this way we managed to solve the mesoscopic mechanism of localized deformation in NiTi....