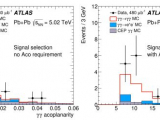
Light-by-light scattering (γγ right arrow γγ) is a quantum-mechanical process that is forbidden in the classical theory of electrodynamics. This reaction is accessible at the Large Hadron Collider thanks to the large electromagnetic field strengths generated by ultra-relativistic colliding lead ions. Using 480 μb−1 of lead–lead collision data recorded at a centre-of-mass energy per nucleon pair of 5.02 TeV by the ATLAS detector, here we report evidence for light-by-light...
You are here
Significant results of scientific activity in year 2017
1/ Evidence for light-by-light scattering in heavy-ion collisions with the ATLAS detector at the LHC
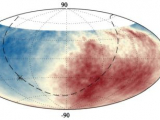
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles arriving from space; some have energies far beyond those that human-made particle accelerators can achieve. The sources of higher-energy cosmic rays remain under debate, although we know that lower-energy cosmic rays come from the solar wind. The Pierre Auger Collaboration reports the observation of thousands of cosmic rays with ultrahigh energies of several exa–electron volts (about a Joule per particle), arriving in a slightly...
One of the most dangerous technical failures of materials is intergranular brittle fracture (temper embrittlement) as it proceeds very quickly and its appearance is often hardly predictable. It is known that this phenomenon is closely related to the chemistry of grain boundaries and to the difference of the segregation energies of the grain boundaries and the free surfaces (Rice–Wang model). To elucidate the effect of individual solutes on embrittlement of various base...
The structural phase transition in hexagonal BaMnO3 occurring at TC=130 K was studied in ceramic samples using electron and x-ray diffraction, second harmonic generation, as well as by dielectric and lattice dynamic spectroscopies. The low-temperature phase (space group P63cm) is ferroelectric with a triplicated unit cell. The phase transition is driven by an optical soft mode from the Brillouin-zone boundary [q=(1/3,1/3,0)]; this mode activates in...
The dielectric permittivity and properties of electrically active lattice resonances in nanotwinned BiFeO3 crystals have been studied theoretically using an earlier established interatomic potential. The results suggest that an array of 71° domain walls with about 2–5 nm spacing enhances the static permittivity of BiFeO3 by more than an order of magnitude. This enhancement is associated with an electrically active excitation, corresponding to a...
6/ Infrared, terahertz, and microwave spectroscopy of the soft and central modes in Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3
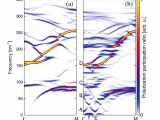
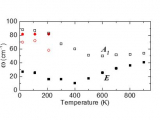
From the new infrared (IR) reflectivity and time-domain terahertz spectra combined with available high-frequency dielectric data above the megahertz range in a broad temperature range of 10 to 900 K, a full picture of the soft- and central-mode behavior in the classical relaxor ferroelectric Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 (PMN) is suggested. A detailed comparison is made with the recent hyper-Raman spectroscopy data [Hehlen et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 117...
The temperature evolution of the structure of Ni50.0Mn28.7Ga21.3 single crystals exhibiting magnetic shape memory effect was investigated near the martensitic transformation by X-ray diffraction. Upon heating, five-layered modulated monoclinic martensite (10M) with nm, nm, nm, and at room temperature (297 K) changed to an intermediate (10M′) phase with nm, nm, and at a few tenths of kelvin below the transformation to austenite at K. This...
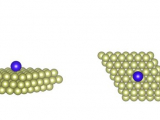
The study of single magnetic rare-earth (RE) atoms adsorbed on metallic and insulating solid surfaces recently became a subject of intense research. These “single-atom” magnets serve as benchmarks in a quest for the ultimate size limit of magnetic information storage. The major advance of observing the magnetic remanence was recently reported for the Ho adatom on MgO substrate. The stable magnetic quantum state of the adatom was found on the time scale of 1500 s at 10 K...
The localization of hydrogen atoms is an essential part of crystal structure analysis, but it is difficult because of their small scattering power. We report the direct localization of hydrogen atoms in nanocrystalline materials, achieved using the recently developed approach of dynamical refinement of precession electron diffraction tomography data. We used this method to locate hydrogen atoms in both an organic (paracetamol) and an inorganic (framework cobalt...
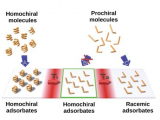
The chirality of molecular structures is paramount in many phenomena, including enantioselective reactions, molecular self-assembly, biological processes and light or electron-spin polarization. Flat prochiral molecules, which are achiral in the gas phase or solution, can exhibit adsorption-induced chirality when deposited on surfaces. The whole array of such molecular adsorbates is naturally racemic as spontaneous global mirror-symmetry breaking is disfavoured. Here we...