Department of environmental geography
| Mgr. Petr Klusacek, Ph.D. | ||
| Filip Alexandrescu, Ph.D. Mgr. Ivan Andrasko, Ph.D. RNDr. Jan Divisek, Ph.D. Mgr. Barbora Duzi, Ph.D. Mgr. Petr Dvorak, Ph.D. RNDr. Bohumil Frantal, Ph.D. Mgr. Petr Halas, Ph.D. Mgr. Eva Kallabova, Ph.D. Doc. RNDr. Karel Kirchner, CSc. | Doc. RNDr. Jaromir Kolejka, CSc. Mgr. Tomas Krejci RNDr. Lucie Kubalikova, Ph.D. Mgr. Frantisek Kuda, Ph.D. Doc. Ing. Jan Lacina, CSc. Mgr. Jiri Maly, Ph.D. Mgr. Stanislav Martinat, Ph.D. Doc. RNDr. Josef Navratil, Ph.D. | Mgr. Eva Novakova RNDr. Stanislav Ondracek RNDr. Robert Osman, Ph.D. Mgr. Pavel Rostinsky, Ph.D. RNDr. Jakub Trojan, MSc. MBA Doc. RNDr. Antonin Vaishar, CSc. RNDr. Jana Zapletalova, CSc. Mgr. Veronika Zuskacova |
Main research topics
The focus of the main research topics is inseparably connected to the environmental geography platform. The aim of the department is to study (by using field mapping and further methods of geographical research) the relations between natural and social processes and the phenomena in landscape in a relatively complex way. From a methodological point of view, the most crucial multidisciplinary character of department can be stressed: in-team researchers with expertise in social geography, sociology, landscape ecology, and physical geography can be found. This situation enables for the creation of research working groups, where all aspects of researched problems can be taken into account. Specific methodological approaches are set during the complex research of natural hazards, i.e. the research of the character of natural hazards, historical impacts and spatial distribution, and temporal development, including research on the impacts of specific phenomenon on society by using methodology of social (human) geography. As methodologically unique, partial approaches to research problems can also be mentioned (i.e. a geobiocenological approach to the study of territorial systems of ecological stability, the concept of post-industrial landscape, the evaluation of geomorphologic localities, studies on the socio-spatial impacts of regeneration and renaturalisation of brownfields, and the social aspects of the development of renewable sources of energy). A large emphasis is placed on empirical research that is necessary in the contemporary world of dynamic changes of reality, from which arise a generalisation of achieved knowledge and head toward a geoinformatical interpretation of research results. The most important research activities have recently been realized in the framework of the following international and national research projects.
Tailored Improvement of Brownfield Regeneration in Europe. The European 7th Framework Project TIMBRE aims to support end-users in overcoming existing barriers by developing and providing customised problem - and target-oriented packages of technologies, approaches, and management tools for the reuse, planning, and remediation of a mega-site. The project team consists of a truly European consortium that integrates 15 partners, which have an international reputation for scientific excellence and a broad practical experience in delivering sustainable brownfield regeneration approaches and technologies to end-users. Moreover, the project is supported by an International Advisory Board of renowned experts from the USA, Great Britain, France and Germany.
This research project, with a wide interdisciplinary background, is trying to find new possibilities in the identification of both proper technologies (e.g. new methods for decontamination of polluted ground water or deconstruction and reuse of material from abandoned buildings) and the decision-making process (tools for stakeholders focused on spreading information for proper decision making). The aim of the research group Institute of Geonics is to identify factors that influence the success of brownfield regeneration projects in four European countries (the Czech Republic, Germany, Poland, Romania) and to develop tools for the prioritisation of areas where brownfields occur. Evaluation is based on multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) by using quantitative (questionnaire surveys, spatial analysis, cluster and factor analysis) and qualitative (expert interviews) methods. Its aim is to assess the main features of brownfield regeneration processes, e.g. the main attributes and typical features of a chosen site/area (history of the area, previous use of land, etc.), the planning and decision-making process (the aim of regeneration, mediation activities, financing of the project), and the evaluation of real and perceived positive and negative impacts and consequences of different types of projects. Results will be used for the verification and relevance of different models for brownfield regeneration.
Energy landscapes: innovation, development and internationalization of research. The project’s objective is to form an interinstitutional and multidisciplinary research and development platform capable of international linkage and competitiveness in the research of energy industry development and its impacts on landscape; to integrate foreign experience and elaborate it into a knowledge portfolio and a theoretical-methodo-logical apparatus which will be utilizable for both the further development and improvement of team expert competencies and a general practice. The means of achieving the objective will include the internationalization of the project team (i.e. an involvement of foreign experts), a transfer of gained experiences by holding common field research activities, an organization of a few thematic workshops and conferences, presentations of gained results at conferences, and a preparation of common publications. Other activities include a variety of specialized trainings for professionals and managers, tutoring of students, and the participation of the partner universities’ students on project research activities.
The destiny of the Czech post-industrial landscape. Within the project, primary attention has been paid to industrial and subsequently post-industrial landscape that is defined by certain typical physiognomic, structural, dynamic, and functional attributes. These attributes are visible in the industrial landscape as 'recent', while in the post-industrial type of landscape these features are more 'fossil'. As a unit, these landscapes can be described by a list of attributes in their synergic contexts. Their common feature is physiognomy given by a character of relief. Accumulation of certain industrial, urban, communication and mining forms of relief is typical and uncovers or covers original units of geological structures.
Land-use in post-industrial landscapes can be characterized by the location of dominant production of off-production built-up areas with typical buildings, wide spread communication spaces, active and passive mining areas, water management facilities, dense residential and other built-up areas and devastated, later abandoned, areas. Within the project, more than 100 objects of post-industrial landscape have been delimited in the Czech Republic. These objects/sites were characterized in-depth, and classified according to the most important types.
Distribution, dynamism and historical aspects of selected natural hazards in the regions of the Czech Republic. Research projects and cooperation with academic institutions, both in the Czech Republic and other countries, have been recently focused on the distribution and dynamism of slope deformations and flooding in Moravia, impacts of land-sliding and flooding as disturbant factors on landscape biocenosis and its diversity. From historical point of view, flooding has been studied with respect to its occurrence, destructive effects, and consequences for the utilisation of landscape. This problem was also studied in the wider area of the Central European region. Achieved research results on the distribution and effects of land-slides and flooding significantly deepened scientific knowledge on relief development and environmental impacts, as well as provided background for the management of such areas.
Cartographical visualisation of the selected issues and phenomenon of the natural and current landscape. In the framework of the research plan of the institute, researchers of the department participated in the creation of a set of thematic and synthetic maps for an atlas of the landscape of the Czech Republic (2009). This national map composition presents the landscape of the Czech Republic for the first time under the new socio-economic conditions after 1989. Our thematic, analytical, and synthetic maps of different scales present the newest knowledge from landscape research activities (especially geomorphology, climatology, land-use). The prepared maps, which can be used not only by experts but by the public as well, can improve the management of landscapes, their development trends, and limitations from the point of future planning. Cartographical visualisation and GIS application are used, for example, by the modelling of the dynamism of the spatial relations of the ecotones, by analysing the location of windmills, by modelling the spatial behaviour of the inhabitants in the urban structures, and in many other issues.
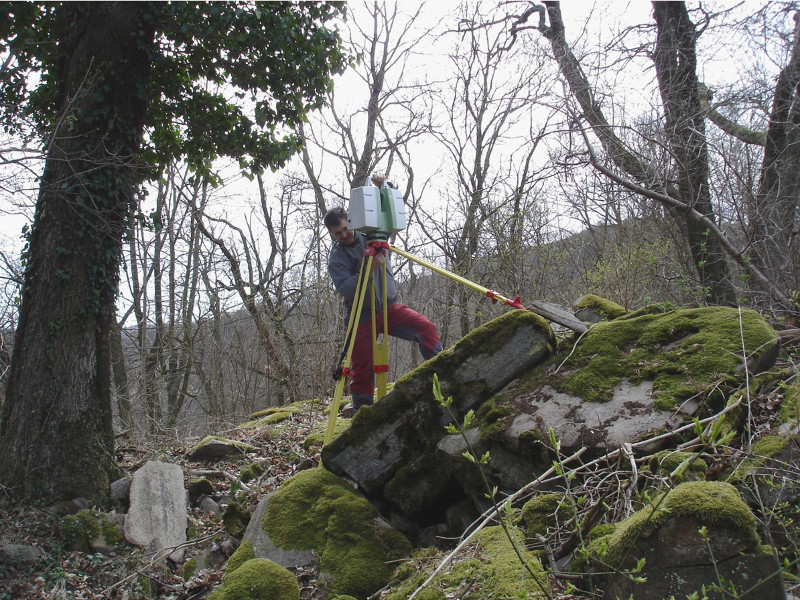
As a very important contribution for the monitoring of dynamics of the contemporary processes in landscape, the gaining of data and its processing by GIS tools, 3D laser scanner (Leica ScanStation C10 with tool for processing of data from global navigation systems and GPS/GNSS Viva NetRover GS08) can be mentioned. Research is focused on the field of dynamical geomorphology and is used in unique localities where nature is strictly protected (Podyji National Park).
Main scientific and application results
As main research results of the Department of Environmental Geography, papers in high quality and scientific reputation journals (see chosen publications) and scientific monographs must be stressed. These publications represent the results of chosen research projects carried out by the department. Between the main applied results, research carried out in cooperation with private companies and public administration should be pointed out. In addition, cooperation with universities on educational projects must be mentioned.
Wind energy in the Czech Republic: an assessment of spatial relations, environmental aspects, and socio-economic context. The monograph brings a relatively complex and comprehensive evaluation of the frequently asked questions related to the development of wind energy in the Czech Republic; the evaluation is based on the analysis of spatial relations, environmental aspects, and the social and economic connections of the given issues. Emphasis is placed on the synthesis of knowledge from abroad and the findings of empirical research. An interdisciplinary approach forms the basis; it involves and systematically evaluates a wide set of mutually related aspects (physical-geographical, environmentally-ecological, human-geographical, and sociological), questions of legislative and economic character, and, finally, issues connected with the impact on the health of the population, quality of life, etc.
Residential Change and Demographic Challenge - The Inner City of East Central Europe in the 21st Century. Going beyond the assumption that East Central European cities are still 'in transition', this book draws on the post-socialist paradigm to ask new questions about the impact of demographic change on residential development in this region. Focusing on four second-order cities in this region, it examines Gdansk and Lodz in Poland, and Brno and Ostrava in the Czech Republic, as examples, and deals with the nexus between urban development and demographic change for the context of East-Central European cities. It provides a framework for linking urban and demographic research. It discusses how residential areas and urban development cope with changes in population development, household types, and different forms of in- and out-migration, and goes on to explore parallels and differences in comparison with broader European patterns.
Selected natural hazards and their impacts in Moravia and Silesia. This book was published by the Institute of Geonics, together with Masaryk University in Brno and Czech Hydrometeorological Institute (2007), and is focused on the complex evaluation of the problems of natural hazards. It consists of features of both hydrometeorological extremes (torrential and long-lasting precipitation, aridity, strong winds, hailstorms, flooding, flash flooding) and geomorphologic extremes (slope processes – land sliding, rock falling, erosion processes – water and wind erosion) and natural seismicity. Large parts of the book are devoted to cartographic visualisation of natural extremes, their temporal and spatial variability, and the impact of natural extremes on population and landscape. Research results in contexts of global changes and global warming are discussed in the conclusion.
Border regions – case studies of chosen peripheral regions of Czech borderlands. The result of research projects funded by the National Program of the Research II – in cooperation with the Sociological Institute of AS CR, the Institute of Current History AS CR, the Economics Institute AS CR, and the Association of the Municipalities of Orlicko – the publication is focused on problems of borderlands in historical and spatial contexts. Emphasis was paid to rural peripheral regions. Borderlands as units were analyzed on microregional levels. Attention was paid to social, economic, and natural problems, as well as historical development after World War II. From a methodological point of view, part of the book is based on the analyses of statistical data, cartographic outputs, and archive materials. Research was also carried out in chosen case study regions.
Congeo conferences. CONGEO 2011 was the 8th presentation of the geographical conferences organized by the Department of Environmental Geography at the Institute of Geonics ASCR (since 1993), which continues the tradition of biennial international meetings of geographers and other social scientists dealing with contemporary regional problems. Last year’s conference was aimed at accelerating international collaboration in research in the field of Energy and Landscape Interrelationships.
A narrow case study of ecosystem monitoring in the deposit area of Rozna and in catchments of the Bukovsky stream. Within this project, 28 test sites for monitoring the ecosystems and vegetation changes were researched using the method of phytocenological shots in an area influenced by the mining and processing of uranium. Specific attention was paid to birds that live in an area with large sludge lagoons and in the Bukov controlled waste dump.
Monitoring of the impact of liquidation of the Reynoutria in the catchment area of the Moravka River. The objective of the research was the monitoring of mechanical and chemical liquidation of the Reynoutria, particularly in the catchments area of the Moravka River, which was proposed to EU Natura 2000 Programme. 16 test sites was founded and monitored by using phytocenological shots. Their analyses enabled deepened specification of relations between invasive neophytes and original bottomland vegetation.
Innovation of Geography education (Geoinnovations). This project’s objectives are focused on the improvement of the quality of university education in the field of geography in Masaryk University in Brno and Palacky University in Olomouc. The objectives will be met by 4 events: (1) the creation of 15 new, and the innovation of 14 existing, courses in Geography, with an emphasis on the development of, modern, updated study materials, e-learning, courses in English, interactive methods of education, strengthening of environmental topics in education, and using GIS tools; (2) the improvement of cooperation with praxis and companies by the organizing of a round table, lectures of experts, the creation of databases for students, etc.; (3) the improvement of expertise of lecturers in Geography (short study stays, courses of expert training, etc.); (4) the strengthening of cooperation between university departments in this country and abroad. Within the project, four partners cooperate. The overall aim is to improve competitiveness and employability of students in the foundation of knowledge.
Other information
|
Recently solved projects ( PDF, 208 kB )
Selected publications ( PDF, 222 kB ) |