From the left: Central clock in the brain - the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN); glial cells in the SCN; lcocomotor activity records of rats; neurons in hippocampus; clock gene expression in the SCN with a phase plot.
Please, consider filing out anonymous questionnaire regarding your chronotype and social jet lag.
In the center of our interest is the endogenous time-keeping system, circadian clock of mammals, including humans. The system temporally regulates rhythmic processes in our body so that they take place at the proper time of day and are optimally synchronized relative to each other.
A failure of the temporal regulation has a negative impact on human health. Using in vivo and in vitro models, we study the molecular mechanisms underlying the circadian clock as well as the resulting physiological and behavioral rhythms.
We focus on the following questions:
- What are the mechanisms for entraining (synchronizing) the circadian system and what are the consequences of its failure?
- How does the circadian system develop and how is it being entrained during ontogeny?
- How is the circadian system of humans entrained in real life conditions, both in health and in disease?
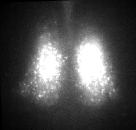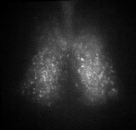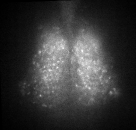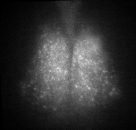
Fig. PER2 protein in the SCN, 7 days ex vivo recording.
Projects
We explore the entrainment of the circadian clock and its disorders on various experimental models in vivo and in vitro.
More
The mammalian biological clock initiates its ontogenesis already during embryonic development in the maternal uterus. Newborn mammals are equipped with clock running in accordance with the maternal clock. We focus on investigating when and how do the newborn clock develop and entrain.
More
Research in our laboratory focuses on the timing system not only in healthy volunteers but also in patients suffering from disorders associated with disrupted sleep pattern. The aim of our projects is to find connections between the functional state of the timing system and those disorders.
More
Achievements
doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04354-7. Misaligned meals become a frequent lifestyle transgression related to current societal pressure imposed on behavior.
More
doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3001637.g005. Our results indicate the importance of a well-functioning maternal biological clock in providing rhythmic environment during the fetal brain development.
More
doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108455. The paper provides new insights into the modulatory role of endocannabinoid signaling during the light entrainment of the SCN.
More
Lucie Olejníková, Lenka Polidarová, Michal Behuliak, Martin Sládek and Alena Sumová.
Circadian alignment in a foster mother improves the offspring’s pathological phenotype. Journal of Physiology (2018), DOI: 10.1113/JP275585.
More
More
Show more
Publications
Sládek; Martin - Liška; Karolína - Houdek; Pavel - Sumová; Alena
.
Modulation of single cell circadian response to NMDA by diacylglycerol lipase inhibition reveals a role of endocannabinoids in light entrainment of the suprachiasmatic nucleus
.
Neuropharmacology. 2021; 185(Mar 1)); 108455
.
IF = 5.250
[ASEP]
[
doi
]
Ralph; M. R. - Shi; S.-Q. - Johnson; C. H. - Houdek; Pavel - Shrestha; T. C. - Crosby; P. - O´Neill; J. S. - Sládek; Martin - Stinchcombe; A. R. - Sumová; Alena
.
Targeted modification of the Per2 clock gene alters circadian function in mPer2(luciferase) (mPer2(Luc)) mice
.
PLoS Computational Biology. 2021; 17(5)); e1008987
.
IF = 4.475
[ASEP]
[
doi
]
Lužná; Vendula - Liška; Karolína - Sládek; Martin - Sumová; Alena
.
Hormonal fine-tuning of clock in decidual region of mouse placenta by dopamine; melatonin; insulin; leptin and ghrelin
.
Placenta. 2021; 108(May); 55-63
.
IF = 3.481
[ASEP]
[
doi
]
Lužná; Vendula - Houdek; Pavel - Liška; Karolína - Sumová; Alena
.
Challenging the Integrity of Rhythmic Maternal Signals Revealed Gene-Specific Responses in the Fetal Suprachiasmatic Nuclei
.
Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2021; 14(Jan 7)); 613531
.
IF = 4.677
[ASEP]
[
doi
]
Liška; Karolína - Sládek; Martin - Čečmanová; Vendula - Sumová; Alena
.
Glucocorticoids reset circadian clock in choroid plexus via period genes
.
Journal of Endocrinology. 2021; 248(2); 155-166
.
IF = 4.286
[ASEP]
[
doi
]
Show more













