Ferroic Multifunctionalities (FerrMion)
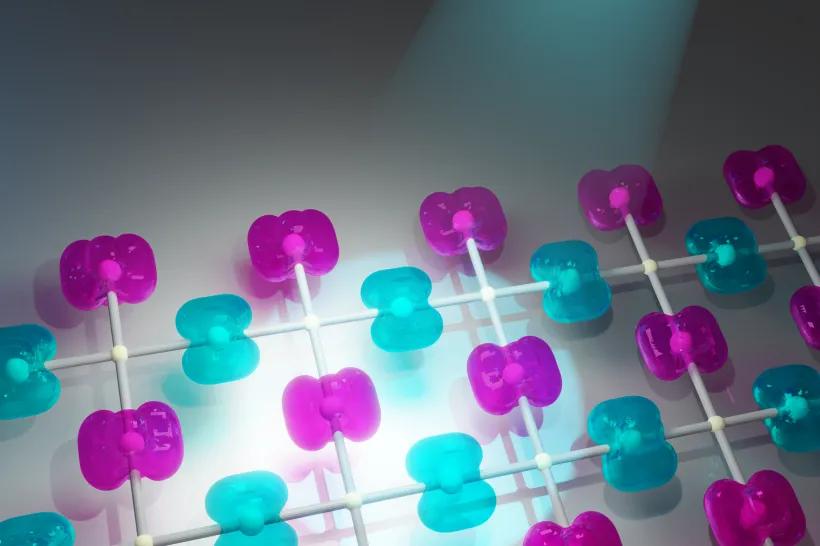
The FerrMion project focuses on research and development of technical applications of ferroic materials, such as ferroelastic alloys with shape memory or multiferroics combining unique electrical, magnetic and mechanical properties. The planned research covers a broad spectrum of physical and technical fields and promises applications in energy, medicine and robotics. As part of the project, a unique 3D atomic probe material characterisation facility, the first of its kind in the Czech Republic, will be commissioned on the premises of the academic institutes in Prague Na Slovance.